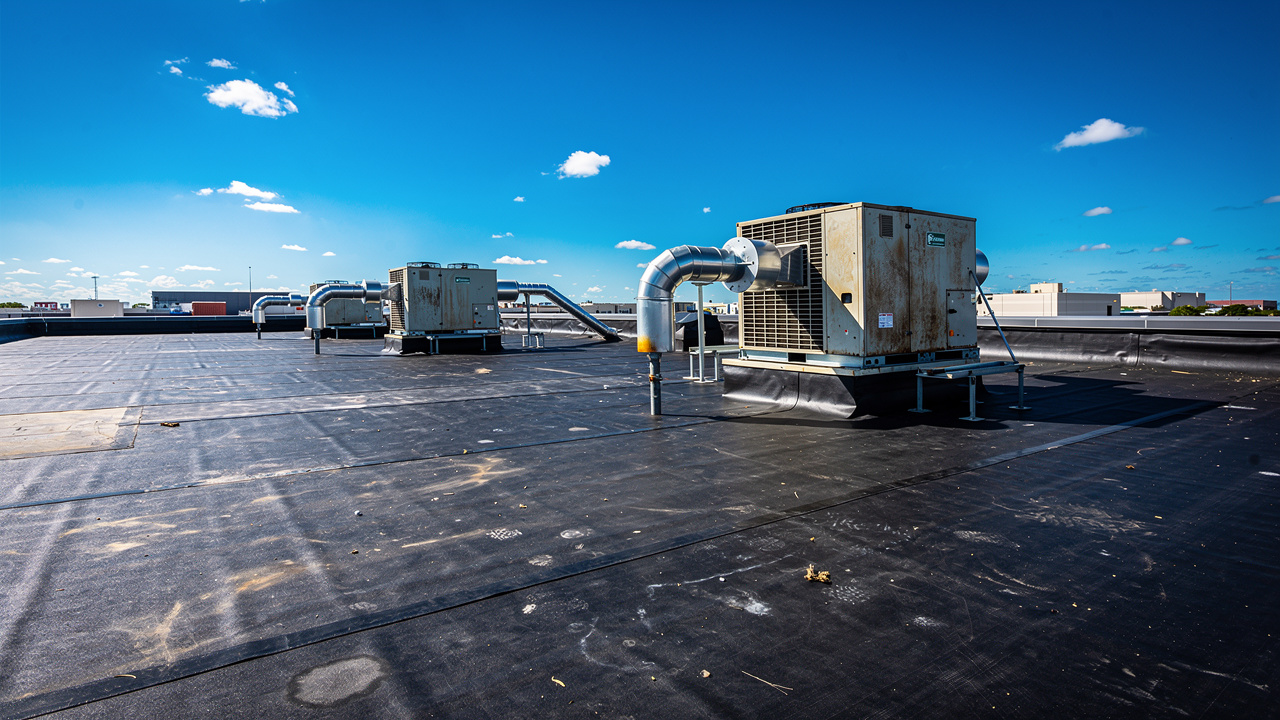
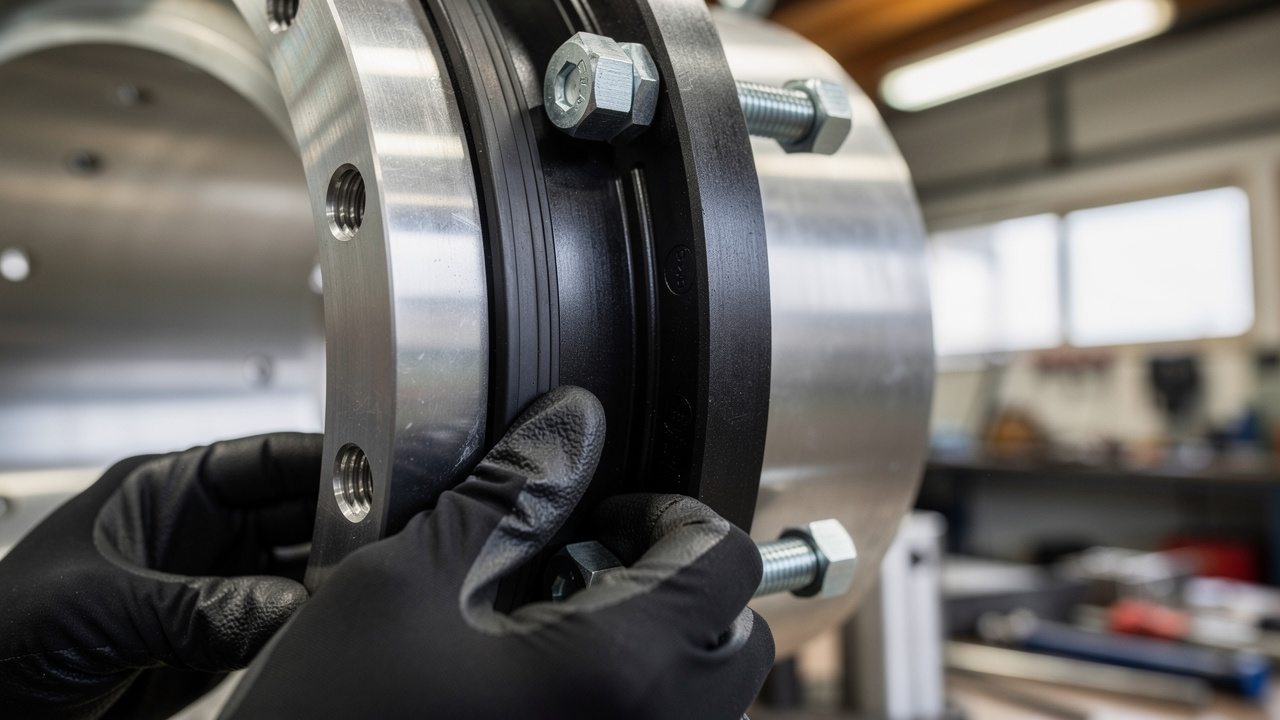
Picture a new commercial tower in Metro Manila where everything looks perfect on opening day. After a few months, complaints start to pile up about humming ceilings, rattling windows, and an odd buzzing in corner offices. The HVAC equipment on the roof runs within its rated capacity, but without proper vibration isolators, every start and stop sends tiny shocks through the structure.
Those small vibrations do more than annoy tenants. They stress motors and bearings, loosen connections, crack concrete over time, and even drag down energy efficiency. Instead of running smoothly, chillers and air handling units fight against misalignment and extra friction. Maintenance teams chase leaks and noisy fans, and the equipment wears out years ahead of schedule.
We see this pattern again and again when vibration control is treated as an optional add‑on instead of part of the HVAC design. With the right vibration isolators under each unit, movement stays where it should be – inside the machine – instead of spreading into beams, floors, and walls. That means longer service life, fewer breakdowns, and lower power bills. It also supports compliance with the Philippine Electrical Code (PEC) and NFPA 110, which already recognize how serious vibration can be, especially for emergency power systems.
In this article, we walk through what vibration isolators are, why HVAC systems depend on them, how to choose the right type, and how proper isolation improves efficiency and lifespan. We also share how we at RK Rubber Enterprise Co. support projects across the Philippines with anti‑vibration pads, mounts, and spring isolators built for local conditions.
Key Takeaways
Before we go deeper, it helps to see the main points in one place. These highlights show why vibration control should stand beside capacity and efficiency in every HVAC design and upgrade plan.
- Proper vibration isolation can extend HVAC equipment life by one‑third or more, often around thirty to fifty percent. That longer life means fewer replacements, less scrap, and more predictable capital planning over many years.
- The Philippine Electrical Code and NFPA 110 call for vibration isolators on emergency power systems. When mechanical rooms combine generators and HVAC equipment, this guidance reinforces the need for proper isolation across the whole setup.
- Elastomeric and spring vibration isolators work best in different ranges of speed and weight. Matching type and rating to actual equipment data is the key to quiet, stable, and efficient operation.
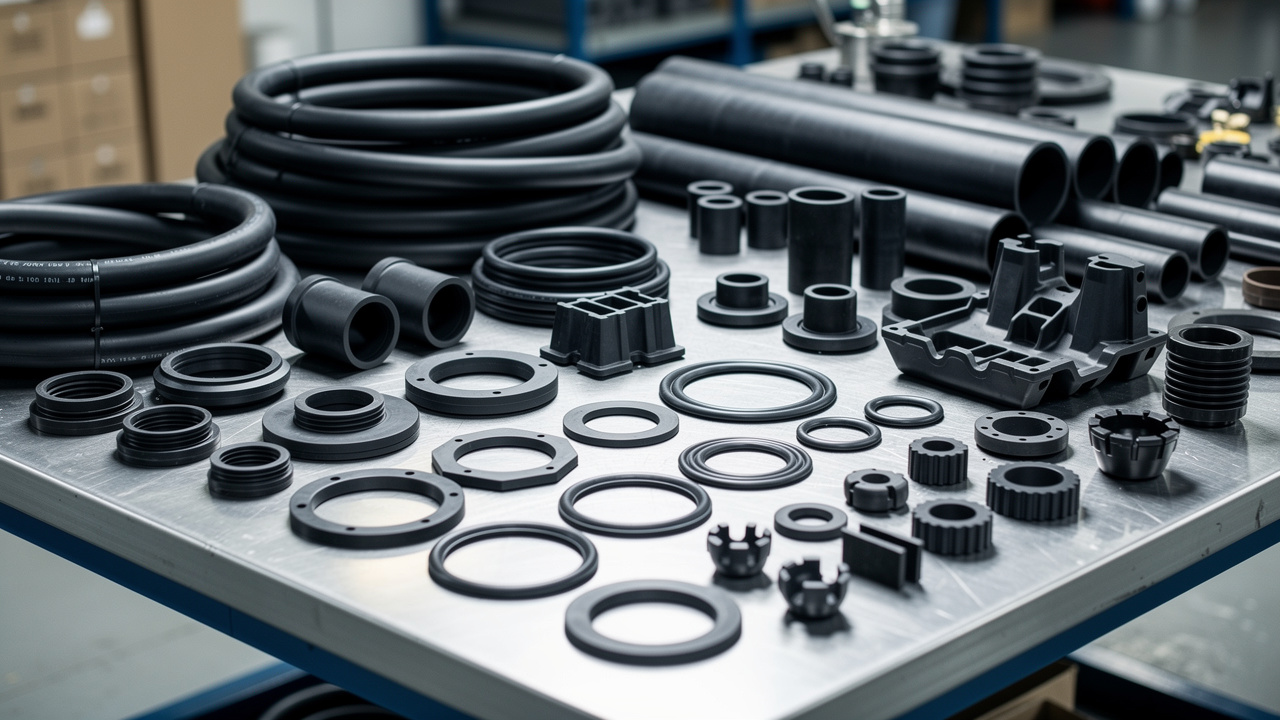
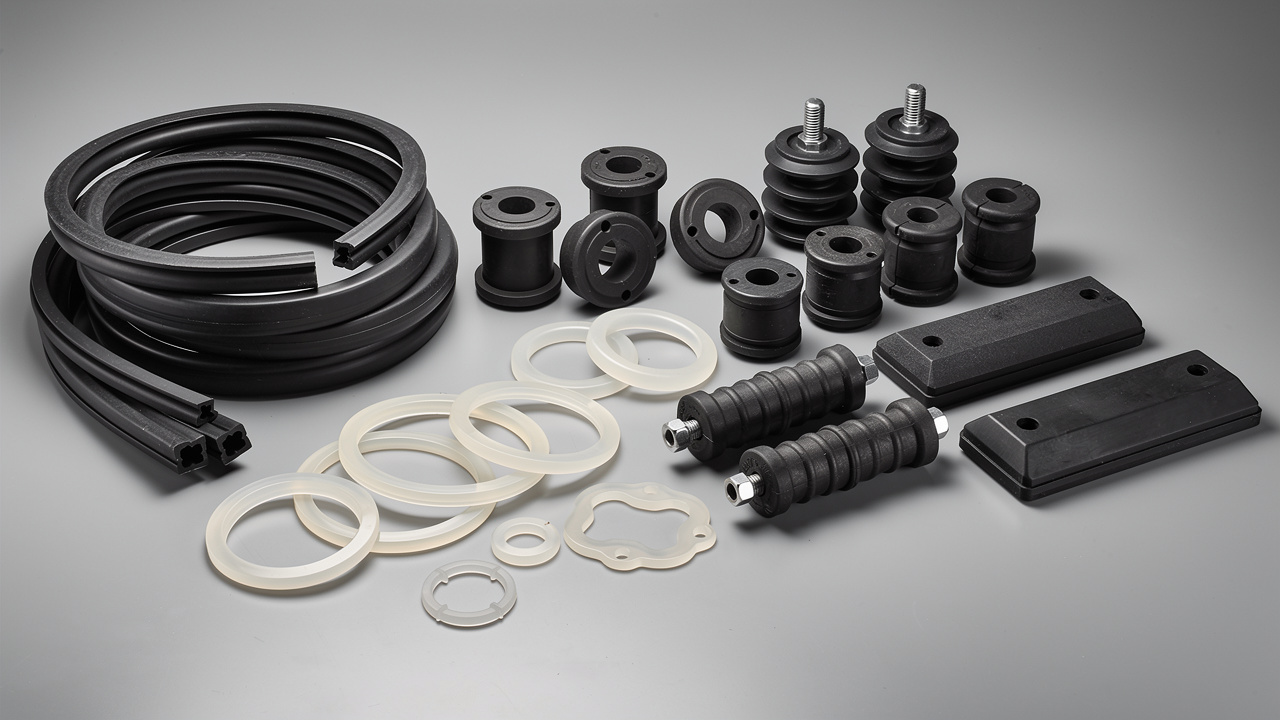
- RK Rubber Enterprise Co. provides a wide range of products, from anti‑vibration rubber pads to engineered metal‑bonded mounts and spring units. This mix allows us to match the isolator design to each chiller, fan, or cooling tower instead of using a one‑size‑fits‑all part.
- Placing vibration isolators between the HVAC equipment and the foundation blocks vibration paths into the structure. This setup cuts noise, protects the building frame, and helps nearby sensitive equipment run correctly.
What Are Vibration Isolators And Why Do HVAC Systems Need Them?
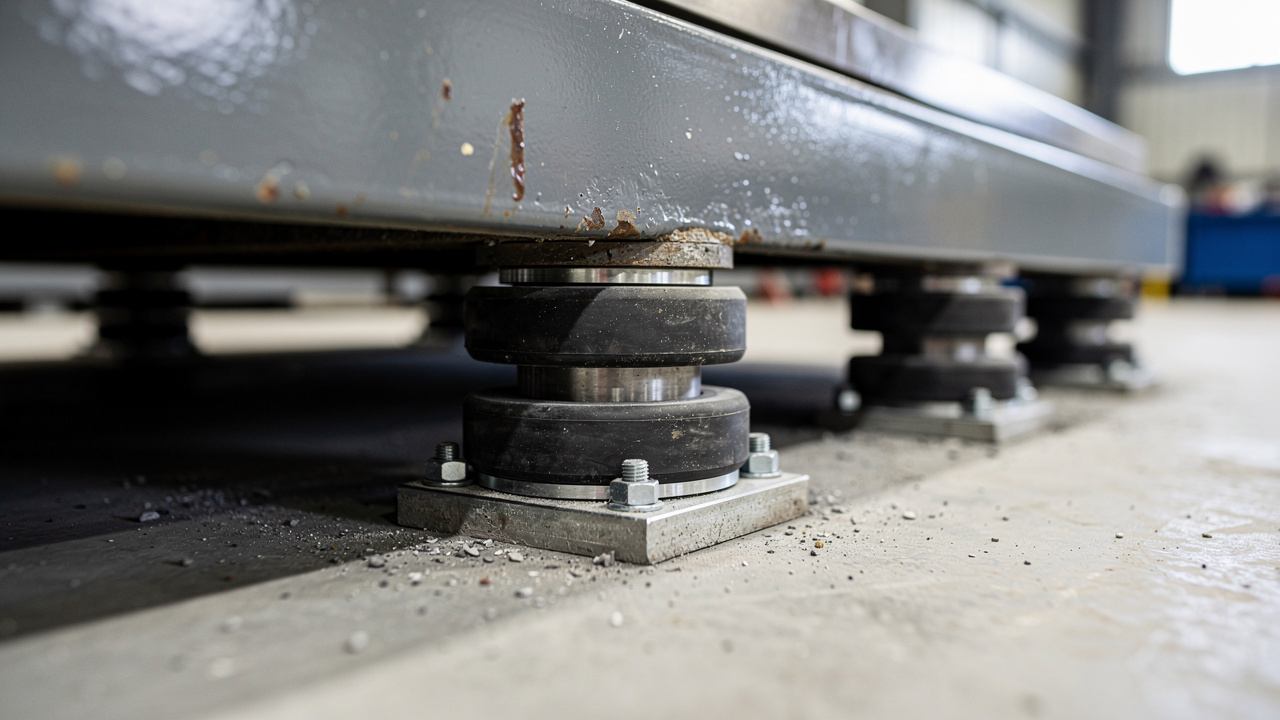
Vibration isolators are engineered parts that sit between a vibrating machine and the structure that supports it. In simple terms, they act like a rubber pads, so the equipment can move slightly without sending that motion straight into beams, slabs, or steel frames. For HVAC systems, these parts are usually rubber‑based mounts, pads, or steel springs designed to work at specific loads and frequencies.
Chillers, air handling units, compressors, and cooling towers all create vibration as motors turn and fans spin. That movement tries to travel from the equipment base through anchor bolts into floors, walls, and columns. Once inside the structure, it spreads out, often showing up as noise or a faint shake far from the machine room.
HVAC equipment needs isolation for three main reasons:
- We protect the equipment itself. Vibration isolators lower the stress on motors, bearings, and compressor assemblies, which reduces misalignment, premature wear, and sudden failures—a principle supported by research on mitigation of structural vibrations in mechanical systems. With less mechanical shock, components keep their factory clearances longer, so the units stay closer to original performance.
- We protect the structural frame. Repeated vibration loads create tiny cycles of stress in concrete and steel. Over time, this can grow from hairline cracks into visible damage around bases and supports. Proper isolation keeps these pulses away from the structure, which helps maintain long‑term strength.
- We protect comfort and quiet inside occupied spaces. Without isolation, structure‑borne vibration turns into noise that travels through slabs and walls. Offices, hotel rooms, and hospital wards can all hear or feel the equipment even several floors away.
“Vibration is one of the most common causes of premature failure in rotating machinery.” — Common teaching in mechanical and rotating equipment design
Industry bodies such as EGSA and NEIS warn against bolting heavy HVAC units directly to floors or pedestals. We follow the same principle and treat vibration isolators as a standard design item, not an afterthought.
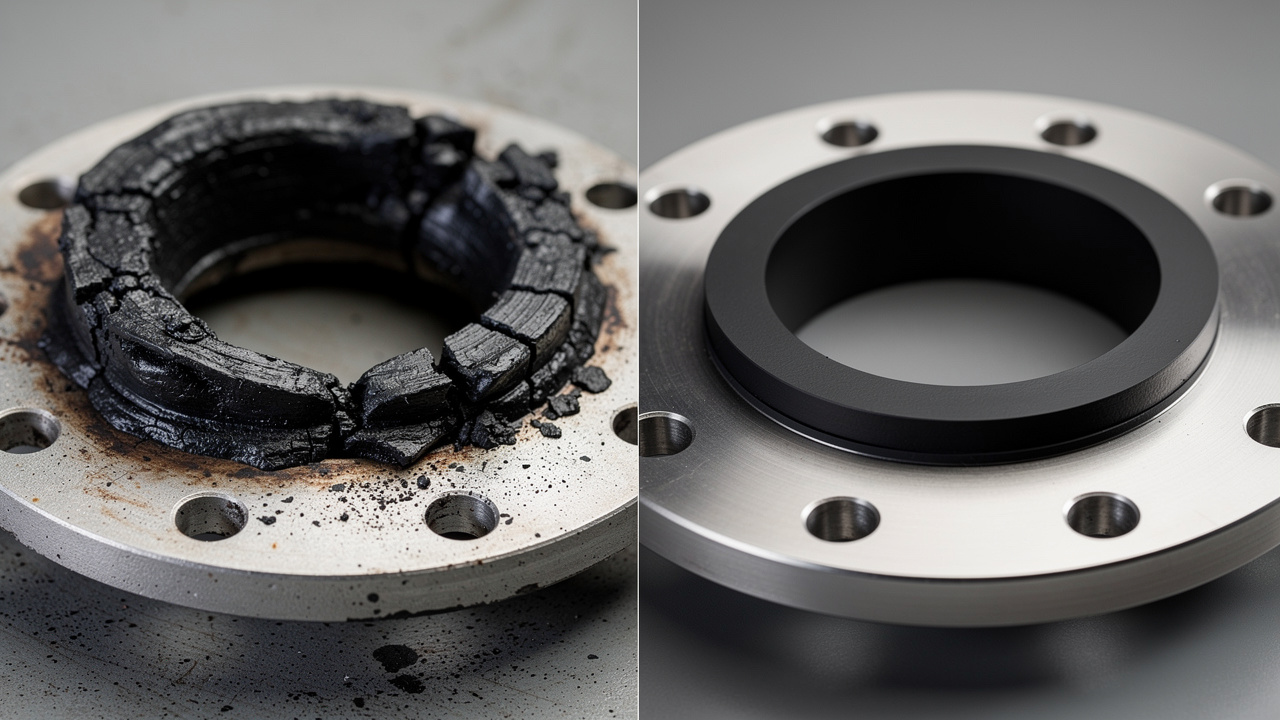
The Hidden Costs Of Poor Vibration Control In HVAC Systems
Poor vibration control rarely fails on day one. Instead, it chips away at performance, comfort, and budgets month after month. When vibration isolators are missing, undersized, or badly installed, the extra movement shows up in four costly ways.
- Premature failure and heavy maintenance.
Constant vibration punishes compressor bearings, motor mounts, and refrigerant lines. Bearings can seize, fan shafts drift out of alignment, and copper lines crack, leading to leaks. Each incident brings unplanned shutdowns, rush parts orders, and overtime labor that far exceed the cost of proper isolation.
- Lower energy efficiency.
As components wear and drift out of alignment, motors need more power to do the same work. Fans may rub or run on poor bearings, and compressors pull extra current. Systems without good isolation often run ten to twenty percent below their rated efficiency, which, at Philippine commercial power rates, adds a serious long‑term burden on operating budgets.
- Gradual structural damage.
Small vibrations create repeated stress cycles in pedestals, beams, and slabs. Micro‑cracks form around anchor points, then widen into visible damage that calls for injection, patching, or even partial rebuilding. These repair projects disrupt operations and cost much more than installing correct vibration isolators during the original works.
- Noise complaints and comfort issues.
Structure‑borne vibration can turn quiet hotel rooms into low‑hum zones and disturb patients in hospitals or residents in condominiums. Tenants may demand rent adjustments or simply move out, which affects property value. On top of that, missed code expectations under PEC Chapter 7 and NFPA 110 can create compliance questions and possible liability if damage or failure occurs.
“If you ignore vibration at commissioning, you pay for it for the rest of the building’s life.” — Saying often heard among maintenance and plant engineers
Types Of Vibration Isolators For HVAC Applications
Choosing the right type of vibration isolator starts with understanding how the HVAC unit behaves. Operating speed, weight, mounting layout, and location all guide the choice. In many building projects, we combine different isolator types so that each piece of equipment gets support that fits its actual job instead of a generic pad.
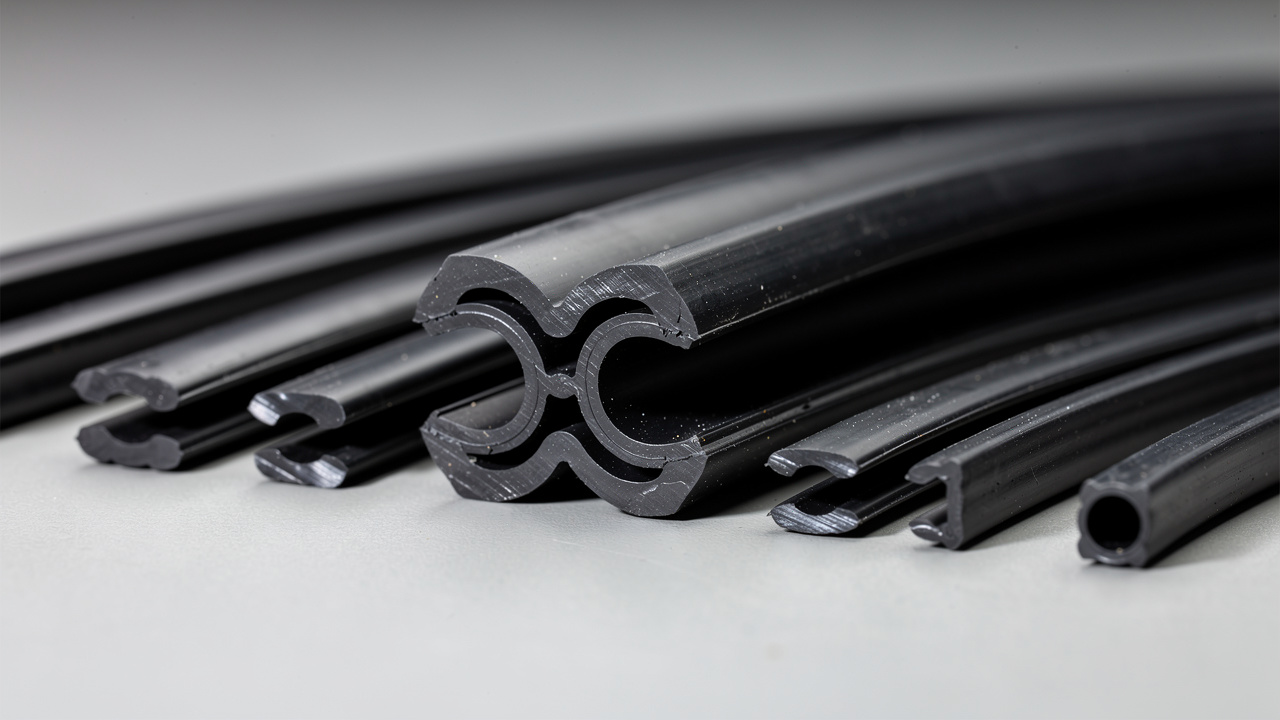
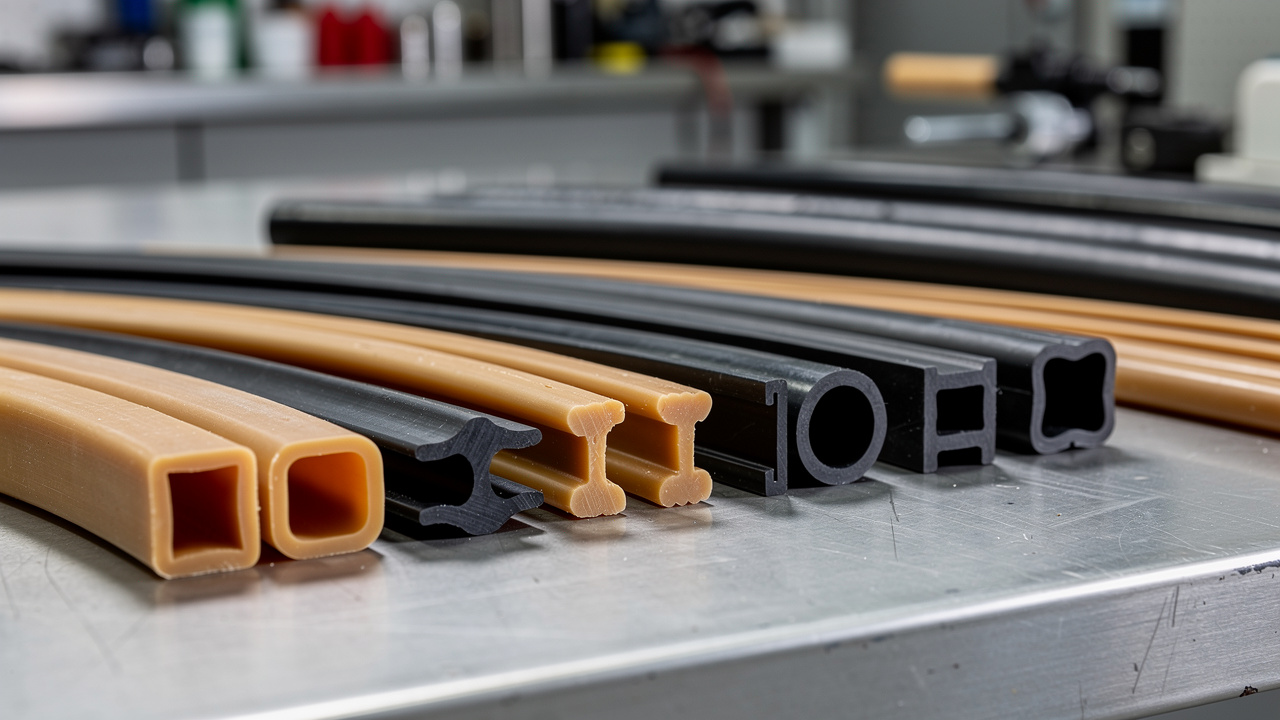
Elastomeric (Rubber) Isolators
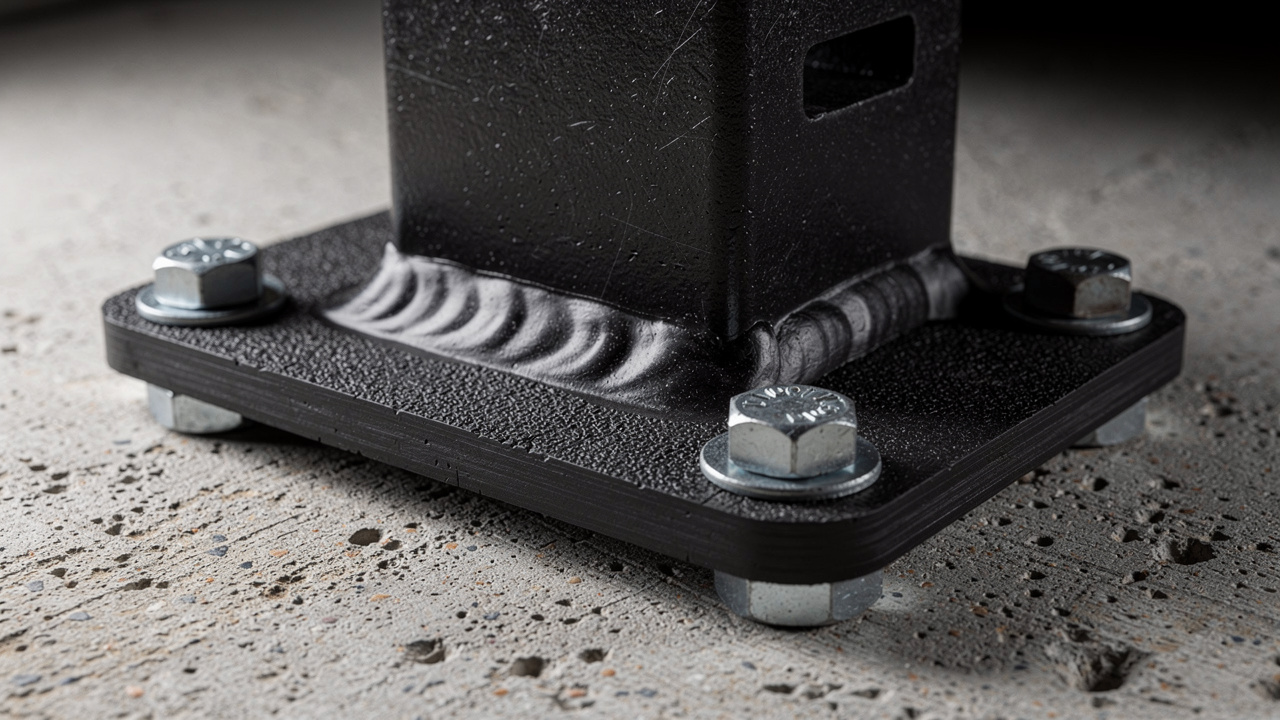

Elastomeric vibration isolators use rubber compounds such as natural rubber, neoprene, or specially mixed blends bonded to steel plates or housings. The rubber works as a flexible layer that compresses and rebounds as the machine moves, with performance characteristics documented in numerical and experimental study of elastomeric behavior under dynamic loads. During this motion, it turns part of the vibrational energy into low‑grade heat, which reduces what reaches the structure.
These isolators work very well for higher operating speeds, where vibration frequencies usually sit above fifteen to twenty hertz. Typical HVAC uses include:
- Air handling units
- Small and medium chillers
- Fan coil units
- Packaged rooftop units
- Many compressor skids
Their compact form makes them a good match for tight mechanical rooms and roof frames with limited height.
Elastomeric mounts are budget‑friendly for moderate loads, easy to install, and effective on high‑frequency vibration from fast‑turning motors and fans. When we build anti‑vibration rubber pads at RK Rubber Enterprise Co., we use advanced compounds designed for long life, high shock absorption, and strong resistance to oils, cleaning chemicals, and weather. That mix fits well with outdoor rooftop equipment that faces Philippine sun, heat, and heavy rain.
Spring Isolators
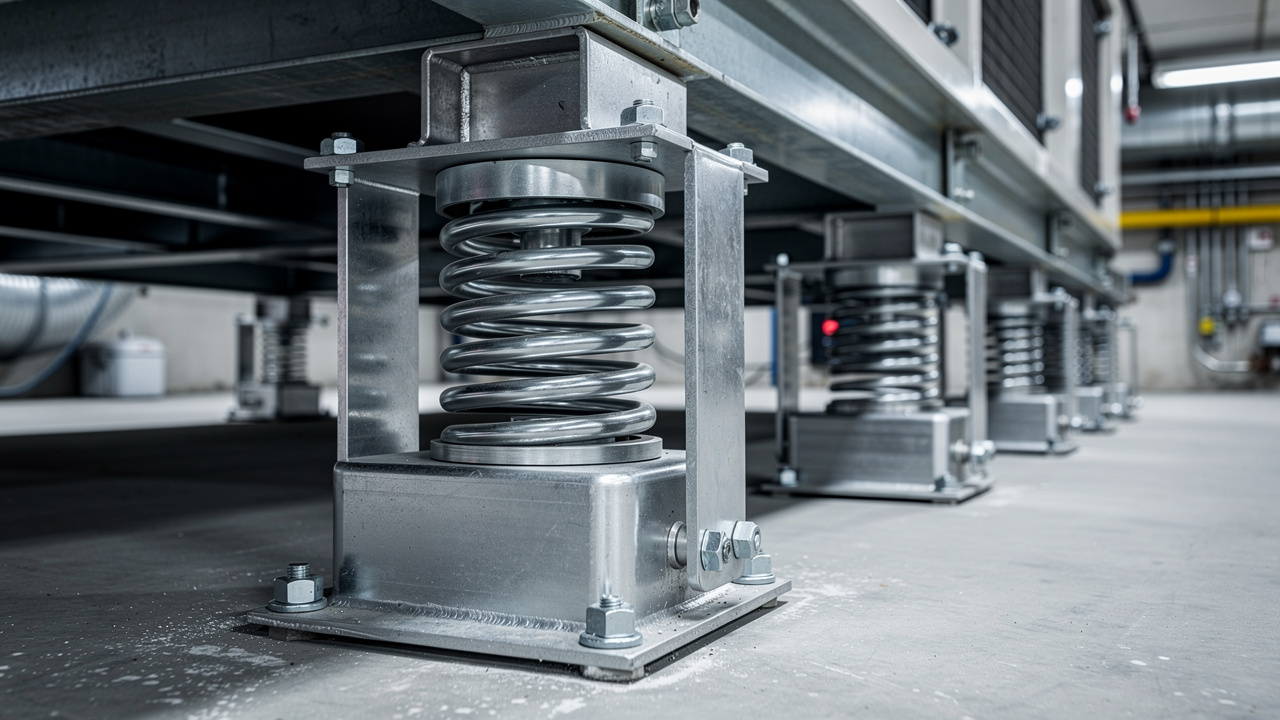

Spring vibration isolators use one or more steel coil springs inside a frame or housing. The equipment weight compresses the spring to a set deflection, which gives the system a low natural frequency. This design is especially good at cutting low‑frequency vibration from large, slow‑speed equipment where rubber alone would not give enough movement.
For HVAC work, spring isolators are common on:
- Heavy chillers
- Cooling towers
- Large air handling systems
- Big rooftop units
These machines often run at lower speeds and higher loads, so their vibration can travel deep into the structure if not handled correctly. Spring units allow greater movement while still keeping the equipment stable and level.
Key advantages include:
- Very good performance at low frequencies
- Strong load capacity for multi‑ton equipment
- Consistent behavior over a long service life
Many designs include adjustment hardware so we can fine‑tune preload and leveling after installation. At RK Rubber Enterprise Co., our spring isolators are built with low natural frequency targets and adjustable settings, which help us match each set to the actual weight and support points of the mechanical rubber products.
Specialized And Hybrid Options
Some HVAC setups need more than a single type of vibration isolator:
- Neoprene pads and strips work well where we need low‑profile support and where oil and chemical resistance matter, such as under smaller pumps or auxiliary equipment.
- Metal‑bonded elastomer mounts provide precise deflection control for equipment that must hold a strict alignment.
- Hybrid systems combine springs with elastomer layers to handle a wide spread of frequencies while still damping noise.
With RK Rubber’s customization capability, we size these parts based on real load points and contact areas rather than guesswork.
Compliance With Philippine Standards: PEC And NFPA 110 Requirements
Code compliance is not just about electrical safety. It also includes how mechanical equipment is supported and isolated. In the Philippines, the Philippine Electrical Code (PEC) places clear attention on emergency and standby power systems, which often share space and foundations with large HVAC equipment.
Chapter 7 of the PEC covers installation, testing, and maintenance for emergency systems and points directly to NFPA 110 as the main reference. This makes NFPA 110 more than a guideline; it becomes the standard that inspectors expect to see followed in hospitals, commercial buildings, and industrial plants with emergency power. Where generator sets and major HVAC equipment sit on common structures, this standard pushes the whole design toward better vibration management.
NFPA 110 Rule 7.5 states that:
“Vibration isolators, as recommended by the manufacturer of the EPS, shall be installed either between the rotating equipment and its skid base or between the skid base and the foundation or inertia base.”
In practice, that means two code‑compliant paths:
- Use isolators between the engine or alternator and the skid, often installed at the factory.
- Place isolators between the skid and the concrete base on site.
Direct bolting of generator sets or similar heavy rotating machines to the foundation fails this expectation and can lead to inspection issues. Non‑compliance may also affect equipment warranties and raise questions if structural damage or failure occurs later.
We always suggest going beyond the bare minimum by following manufacturer isolation guidance for all major HVAC units, not just emergency equipment. Our team at RK Rubber Enterprise Co. supports this process with product selection help, drawings, and data that make it easier to document compliance.
How To Select The Right Vibration Isolators For Your HVAC System
Good results start with the right data. Picking vibration isolators based only on rough weight guesses or catalog pictures often leads to underperformance. We follow a simple framework that any facility manager or engineer can use as a checklist.
Step 1 – Determine Equipment Operating Frequency
Look at fan and motor speed in revolutions per minute and convert that to hertz by dividing by sixty. Higher frequencies often point to elastomeric isolators, especially above about fifteen hertz. Lower speeds, especially on big chillers and towers, usually call for spring isolators with enough deflection to sit well below the disturbing frequency.
Step 2 – Calculate Total Load And How It Is Shared
Include the full operating weight of the HVAC unit, not just the dry weight on the nameplate. That means adding refrigerant, oil, and any accessories. Then check the base frame and mounting bolt layout to understand how this weight spreads across each isolator. Undersized mounts can bottom out, while oversized ones may not deflect enough to work properly.
Step 3 – Define The Isolation Level You Need
General comfort cooling for offices may work well with about eighty‑five to ninety percent isolation, following established vibration isolation use guidelines for commercial applications. Hospitals, data centers, and research facilities may need ninety‑five percent or more. Higher targets push designs toward spring isolators and more deflection, especially at low frequencies.
Step 4 – Consider The Environment
Philippine heat, humidity, UV exposure, and occasional flooding all affect material choice. Check for outdoor or rooftop placement, exposure to oils or chemicals, and temperature swings in mechanical rooms. Rubber compounds must stand up to these conditions without hardening or creeping.
Step 5 – Review Space And Support Limits
Available height, base footprint, and foundation capacity shape the final choice. Some spring isolation systems need more clearance, while low‑profile neoprene pads work in tight spaces. Also plan access so maintenance teams can inspect or change isolators without major disassembly.
Step 6 – Match Hardness And Dynamic Stiffness
For elastomeric mounts, Shore hardness affects how much they deflect under load and where the natural frequency sits. Dynamic stiffness tells us how the mount behaves under actual vibration, not just static weight. At RK Rubber Enterprise Co., we use this data to select or customize rubber cushion so the system avoids resonance and meets target isolation.
When customers share accurate load and layout data, we can provide clear recommendations and test information that support both performance and compliance documentation.
Measurable Benefits: How Proper Vibration Isolation Improves HVAC Performance
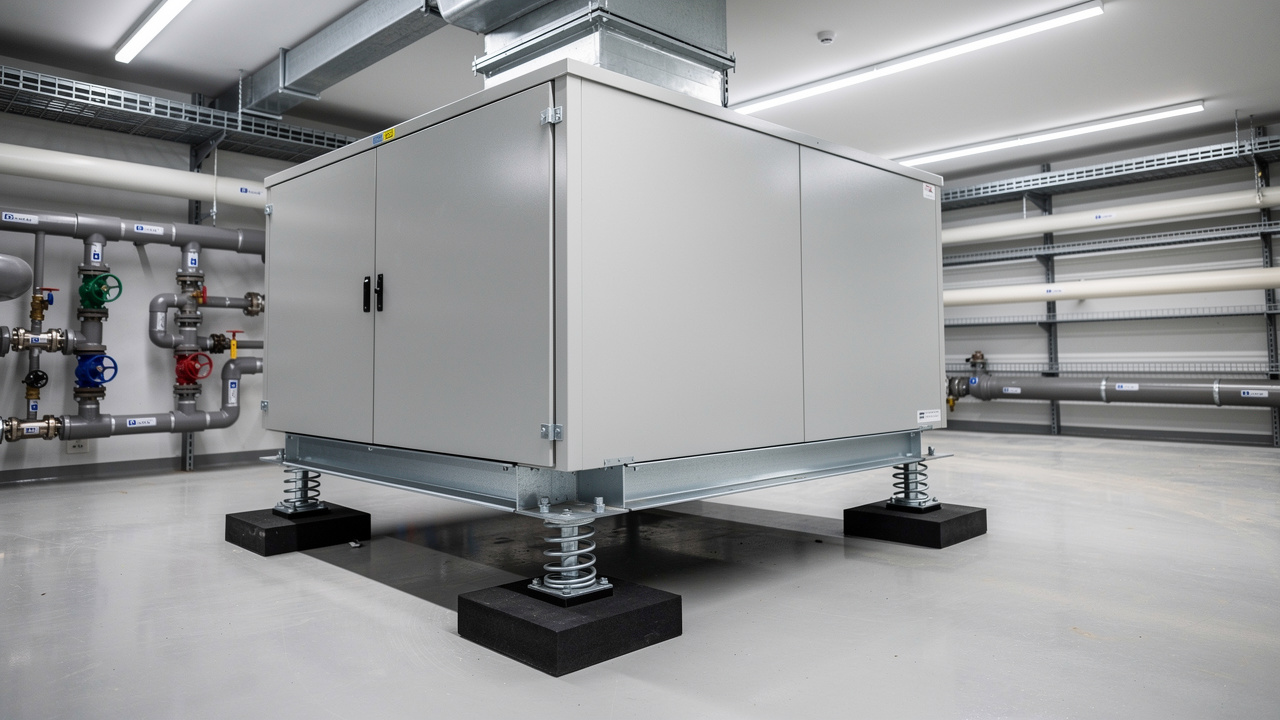

When vibration isolators are selected and installed correctly, the gains show up in both technical reports and financial statements. Many plants and buildings move from constant repairs to stable, predictable HVAC operation once proper isolation is in place.
Key measurable benefits include:
- Longer equipment lifespan.
With lower mechanical stress on bearings, shafts, and compressor internals, HVAC units can run thirty to fifty percent longer before major overhaul or replacement. Over a ten‑ to fifteen‑year planning window, this can keep expensive chillers and large fans in service well past the point where poorly isolated units would already be replaced.
- Lower maintenance costs.
Better isolation means fewer bearing changes, fewer refrigerant leaks due to cracked lines, and less time spent on repeated alignment work. Many facilities report maintenance savings in the range of twenty to forty percent for well‑isolated systems, along with fewer emergency callouts and less unplanned downtime during peak cooling months.
- Improved energy performance.
Machines that stay in alignment and operate on healthy bearings use less power. With proper vibration control, it is common to see five to fifteen percent better energy use compared with similar equipment installed on hard mounts. With local electricity costs, even the lower end of that range gives a strong payback.
On top of this, stable isolation supports:
- More consistent temperatures and humidity
- Fewer nuisance trips and control issues
- Quieter spaces and better comfort for occupants
- Less risk of damage to foundations and nearby sensitive equipment
RK Rubber Enterprise Co. supports these gains with high‑quality rubber compounds and tested spring designs that hold their properties over many years in Philippine conditions.
Conclusion
Good HVAC design is about more than picking the right capacity and controls. Without proper vibration isolation, even the best chiller or air handling unit can become a source of wasted energy, early failure, and ongoing complaints. Well‑chosen vibration isolators keep movement inside the machine, protect the building, and help systems run closer to their rated performance for a longer time.
By investing in quality isolation, we protect both the equipment and the structure that supports it. That means fewer major repairs, less noise in offices or hotel rooms, and a longer interval before expensive replacements appear in the budget. When we factor in lower energy use and reduced maintenance, the initial cost of good isolators often pays back many times over the life of the HVAC plant.
For facilities in the Philippines, the PEC and NFPA 110 already recognize how important proper vibration control is, especially around emergency power systems. Bringing the same care to all major HVAC equipment keeps projects safer, quieter, and easier to justify during audits and inspections. Facility managers, engineers, and contractors should review existing installations, check for proper vibration control, and specify isolation from the start on new projects.
At RK Rubber Enterprise Co., we support this work with a wide product range, from anti‑vibration rubber pads and neoprene strips to engineered metal‑bonded mounts and spring isolators. Our team helps match each product to real loads and conditions, giving customers both reliable performance and peace of mind.
FAQs
Question 1: What Is The Difference Between Elastomeric And Spring Vibration Isolators For HVAC Systems?
Elastomeric vibration isolators use rubber compounds to absorb higher‑frequency vibration, usually above fifteen to twenty hertz. They suit smaller and medium HVAC units, such as compressors, fan coil units, and packaged rooftop systems, where loads and deflections stay moderate. Spring isolators use steel coils to handle lower‑frequency vibration and heavier equipment, such as chillers and cooling towers. They provide greater deflection and better isolation for slow‑speed machines. The choice depends on operating speed, weight, and how much isolation the project needs, and RK Rubber Enterprise Co. offers both types with options for customization.
Question 2: Are Vibration Isolators Required By Law In The Philippines For HVAC Installations?
For emergency power supply systems, yes. PEC Chapter 7 points to NFPA 110, whose Rule 7.5 calls for vibration isolators between the rotating equipment and skid, or between the skid and the foundation. General HVAC equipment outside emergency systems may not always be named directly in the same way. However, manufacturers and industry groups such as EGSA and NEIS strongly discourage direct bolting without isolation. Following their guidance protects structural and equipment warranties and reduces the risk of damage or liability.
Question 3: How Do I Know What Size And Type Of Vibration Isolator I Need For My HVAC Equipment?
Sizing starts with accurate equipment data. You need the full operating weight including refrigerant, oil, and accessories; the rotating speed of fans or compressors; and the mounting layout. From there, check how weight is shared across the support points and what isolation level is needed for the space below or around the unit. Undersized isolators will compress too much and lose their function, while oversized units may not deflect enough and can cause instability. The best path is to consult manufacturer data and then work with a partner like RK Rubber Enterprise Co., where our technical team uses real load point measurements and site conditions to recommend the correct type and rating.
Question 4: Can Vibration Isolators Really Extend HVAC Equipment Lifespan And Reduce Energy Costs?
Yes, and the gains are measurable. By cutting vibration levels, you reduce wear on bearings, motors, and compressor parts, which can extend service life by thirty to fifty percent compared with rigid mounting. That same reduction in friction and misalignment often improves energy performance by about five to fifteen percent, because motors do not fight extra resistance. Maintenance needs usually drop by twenty to forty percent as leaks, bearing failures, and misalignment problems become less common. In many projects, the cost of proper vibration isolators pays back within two to three years through combined savings, especially when using RK Rubber’s durable compounds and tested designs.
Question 5: How Often Should Vibration Isolators Be Inspected Or Replaced?
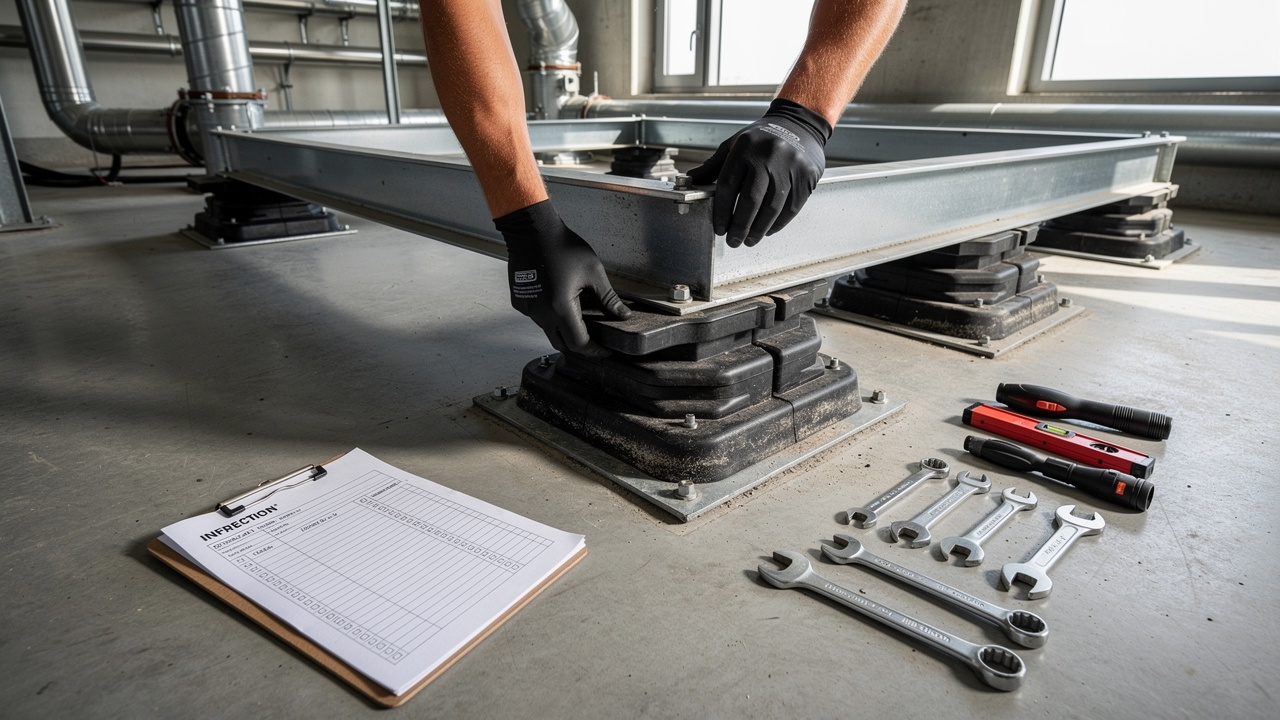

We suggest at least one visual inspection each year. During this check, look for cracks, hardening, or excessive compression in rubber parts and make sure the equipment remains level on its supports. Quality elastomeric mounts often last ten to fifteen years, while well‑protected spring isolators can serve for fifteen to twenty years or more. Signs that replacement is needed include visible cracking, permanent flattening beyond design limits, and noticeable increases in transmitted vibration or noise. RK Rubber Enterprise Co. designs its products with strong resistance to weather, corrosion, and mechanical shock, which supports long service life under Philippine conditions.
Introduction
Picture a new commercial tower in Metro Manila where everything looks perfect on opening day. After a few months, complaints start to pile up about humming ceilings, rattling windows, and an odd buzzing in corner offices. The HVAC equipment on the roof runs within its rated capacity, but without proper vibration isolators, every start and stop sends tiny shocks through the structure.
Those small vibrations do more than annoy tenants. They stress motors and bearings, loosen connections, crack concrete over time, and even drag down energy efficiency. Instead of running smoothly, chillers and air handling units fight against misalignment and extra friction. Maintenance teams chase leaks and noisy fans, and the equipment wears out years ahead of schedule.
We see this pattern again and again when vibration control is treated as an optional add‑on instead of part of the HVAC design. With the right vibration isolators under each unit, movement stays where it should be – inside the machine – instead of spreading into beams, floors, and walls. That means longer service life, fewer breakdowns, and lower power bills. It also supports compliance with the Philippine Electrical Code (PEC) and NFPA 110, which already recognize how serious vibration can be, especially for emergency power systems.
In this article, we walk through what vibration isolators are, why HVAC systems depend on them, how to choose the right type, and how proper isolation improves efficiency and lifespan. We also share how we at RK Rubber Enterprise Co. support projects across the Philippines with anti‑vibration pads, mounts, and spring isolators built for local conditions.
Key Takeaways
Before we go deeper, it helps to see the main points in one place. These highlights show why vibration control should stand beside capacity and efficiency in every HVAC design and upgrade plan.
- Proper vibration isolation can extend HVAC equipment life by one‑third or more, often around thirty to fifty percent. That longer life means fewer replacements, less scrap, and more predictable capital planning over many years.
- The Philippine Electrical Code and NFPA 110 call for vibration isolators on emergency power systems. When mechanical rooms combine generators and HVAC equipment, this guidance reinforces the need for proper isolation across the whole setup.
- Elastomeric and spring vibration isolators work best in different ranges of speed and weight. Matching type and rating to actual equipment data is the key to quiet, stable, and efficient operation.
- RK Rubber Enterprise Co. provides a wide range of products, from anti‑vibration rubber pads to engineered metal‑bonded mounts and spring units. This mix allows us to match the isolator design to each chiller, fan, or cooling tower instead of using a one‑size‑fits‑all part.
- Placing vibration isolators between the HVAC equipment and the foundation blocks vibration paths into the structure. This setup cuts noise, protects the building frame, and helps nearby sensitive equipment run correctly.
What Are Vibration Isolators And Why Do HVAC Systems Need Them?
Vibration isolators are engineered parts that sit between a vibrating machine and the structure that supports it. In simple terms, they act like a rubber pads, so the equipment can move slightly without sending that motion straight into beams, slabs, or steel frames. For HVAC systems, these parts are usually rubber‑based mounts, pads, or steel springs designed to work at specific loads and frequencies.
Chillers, air handling units, compressors, and cooling towers all create vibration as motors turn and fans spin. That movement tries to travel from the equipment base through anchor bolts into floors, walls, and columns. Once inside the structure, it spreads out, often showing up as noise or a faint shake far from the machine room.
HVAC equipment needs isolation for three main reasons:
- We protect the equipment itself. Vibration isolators lower the stress on motors, bearings, and compressor assemblies, which reduces misalignment, premature wear, and sudden failures—a principle supported by research on mitigation of structural vibrations in mechanical systems. With less mechanical shock, components keep their factory clearances longer, so the units stay closer to original performance.
- We protect the structural frame. Repeated vibration loads create tiny cycles of stress in concrete and steel. Over time, this can grow from hairline cracks into visible damage around bases and supports. Proper isolation keeps these pulses away from the structure, which helps maintain long‑term strength.
- We protect comfort and quiet inside occupied spaces. Without isolation, structure‑borne vibration turns into noise that travels through slabs and walls. Offices, hotel rooms, and hospital wards can all hear or feel the equipment even several floors away.
“Vibration is one of the most common causes of premature failure in rotating machinery.” — Common teaching in mechanical and rotating equipment design
Industry bodies such as EGSA and NEIS warn against bolting heavy HVAC units directly to floors or pedestals. We follow the same principle and treat vibration isolators as a standard design item, not an afterthought.
The Hidden Costs Of Poor Vibration Control In HVAC Systems
Poor vibration control rarely fails on day one. Instead, it chips away at performance, comfort, and budgets month after month. When vibration isolators are missing, undersized, or badly installed, the extra movement shows up in four costly ways.
- Premature failure and heavy maintenance.
Constant vibration punishes compressor bearings, motor mounts, and refrigerant lines. Bearings can seize, fan shafts drift out of alignment, and copper lines crack, leading to leaks. Each incident brings unplanned shutdowns, rush parts orders, and overtime labor that far exceed the cost of proper isolation.
- Lower energy efficiency.
As components wear and drift out of alignment, motors need more power to do the same work. Fans may rub or run on poor bearings, and compressors pull extra current. Systems without good isolation often run ten to twenty percent below their rated efficiency, which, at Philippine commercial power rates, adds a serious long‑term burden on operating budgets.
- Gradual structural damage.
Small vibrations create repeated stress cycles in pedestals, beams, and slabs. Micro‑cracks form around anchor points, then widen into visible damage that calls for injection, patching, or even partial rebuilding. These repair projects disrupt operations and cost much more than installing correct vibration isolators during the original works.
- Noise complaints and comfort issues.
Structure‑borne vibration can turn quiet hotel rooms into low‑hum zones and disturb patients in hospitals or residents in condominiums. Tenants may demand rent adjustments or simply move out, which affects property value. On top of that, missed code expectations under PEC Chapter 7 and NFPA 110 can create compliance questions and possible liability if damage or failure occurs.
“If you ignore vibration at commissioning, you pay for it for the rest of the building’s life.” — Saying often heard among maintenance and plant engineers
Types Of Vibration Isolators For HVAC Applications
Choosing the right type of vibration isolator starts with understanding how the HVAC unit behaves. Operating speed, weight, mounting layout, and location all guide the choice. In many building projects, we combine different isolator types so that each piece of equipment gets support that fits its actual job instead of a generic pad.
Elastomeric (Rubber) Isolators

Elastomeric vibration isolators use rubber compounds such as natural rubber, neoprene, or specially mixed blends bonded to steel plates or housings. The rubber works as a flexible layer that compresses and rebounds as the machine moves, with performance characteristics documented in numerical and experimental study of elastomeric behavior under dynamic loads. During this motion, it turns part of the vibrational energy into low‑grade heat, which reduces what reaches the structure.
These isolators work very well for higher operating speeds, where vibration frequencies usually sit above fifteen to twenty hertz. Typical HVAC uses include:
- Air handling units
- Small and medium chillers
- Fan coil units
- Packaged rooftop units
- Many compressor skids
Their compact form makes them a good match for tight mechanical rooms and roof frames with limited height.
Elastomeric mounts are budget‑friendly for moderate loads, easy to install, and effective on high‑frequency vibration from fast‑turning motors and fans. When we build anti‑vibration rubber pads at RK Rubber Enterprise Co., we use advanced compounds designed for long life, high shock absorption, and strong resistance to oils, cleaning chemicals, and weather. That mix fits well with outdoor rooftop equipment that faces Philippine sun, heat, and heavy rain.
Spring Isolators

Spring vibration isolators use one or more steel coil springs inside a frame or housing. The equipment weight compresses the spring to a set deflection, which gives the system a low natural frequency. This design is especially good at cutting low‑frequency vibration from large, slow‑speed equipment where rubber alone would not give enough movement.
For HVAC work, spring isolators are common on:
- Heavy chillers
- Cooling towers
- Large air handling systems
- Big rooftop units
These machines often run at lower speeds and higher loads, so their vibration can travel deep into the structure if not handled correctly. Spring units allow greater movement while still keeping the equipment stable and level.
Key advantages include:
- Very good performance at low frequencies
- Strong load capacity for multi‑ton equipment
- Consistent behavior over a long service life
Many designs include adjustment hardware so we can fine‑tune preload and leveling after installation. At RK Rubber Enterprise Co., our spring isolators are built with low natural frequency targets and adjustable settings, which help us match each set to the actual weight and support points of the mechanical rubber products.
Specialized And Hybrid Options
Some HVAC setups need more than a single type of vibration isolator:
- Neoprene pads and strips work well where we need low‑profile support and where oil and chemical resistance matter, such as under smaller pumps or auxiliary equipment.
- Metal‑bonded elastomer mounts provide precise deflection control for equipment that must hold a strict alignment.
- Hybrid systems combine springs with elastomer layers to handle a wide spread of frequencies while still damping noise.
With RK Rubber’s customization capability, we size these parts based on real load points and contact areas rather than guesswork.
Compliance With Philippine Standards: PEC And NFPA 110 Requirements
Code compliance is not just about electrical safety. It also includes how mechanical equipment is supported and isolated. In the Philippines, the Philippine Electrical Code (PEC) places clear attention on emergency and standby power systems, which often share space and foundations with large HVAC equipment.
Chapter 7 of the PEC covers installation, testing, and maintenance for emergency systems and points directly to NFPA 110 as the main reference. This makes NFPA 110 more than a guideline; it becomes the standard that inspectors expect to see followed in hospitals, commercial buildings, and industrial plants with emergency power. Where generator sets and major HVAC equipment sit on common structures, this standard pushes the whole design toward better vibration management.
NFPA 110 Rule 7.5 states that:
“Vibration isolators, as recommended by the manufacturer of the EPS, shall be installed either between the rotating equipment and its skid base or between the skid base and the foundation or inertia base.”
In practice, that means two code‑compliant paths:
- Use isolators between the engine or alternator and the skid, often installed at the factory.
- Place isolators between the skid and the concrete base on site.
Direct bolting of generator sets or similar heavy rotating machines to the foundation fails this expectation and can lead to inspection issues. Non‑compliance may also affect equipment warranties and raise questions if structural damage or failure occurs later.
We always suggest going beyond the bare minimum by following manufacturer isolation guidance for all major HVAC units, not just emergency equipment. Our team at RK Rubber Enterprise Co. supports this process with product selection help, drawings, and data that make it easier to document compliance.
How To Select The Right Vibration Isolators For Your HVAC System
Good results start with the right data. Picking vibration isolators based only on rough weight guesses or catalog pictures often leads to underperformance. We follow a simple framework that any facility manager or engineer can use as a checklist.
Step 1 – Determine Equipment Operating Frequency
Look at fan and motor speed in revolutions per minute and convert that to hertz by dividing by sixty. Higher frequencies often point to elastomeric isolators, especially above about fifteen hertz. Lower speeds, especially on big chillers and towers, usually call for spring isolators with enough deflection to sit well below the disturbing frequency.
Step 2 – Calculate Total Load And How It Is Shared
Include the full operating weight of the HVAC unit, not just the dry weight on the nameplate. That means adding refrigerant, oil, and any accessories. Then check the base frame and mounting bolt layout to understand how this weight spreads across each isolator. Undersized mounts can bottom out, while oversized ones may not deflect enough to work properly.
Step 3 – Define The Isolation Level You Need
General comfort cooling for offices may work well with about eighty‑five to ninety percent isolation, following established vibration isolation use guidelines for commercial applications. Hospitals, data centers, and research facilities may need ninety‑five percent or more. Higher targets push designs toward spring isolators and more deflection, especially at low frequencies.
Step 4 – Consider The Environment
Philippine heat, humidity, UV exposure, and occasional flooding all affect material choice. Check for outdoor or rooftop placement, exposure to oils or chemicals, and temperature swings in mechanical rooms. Rubber compounds must stand up to these conditions without hardening or creeping.
Step 5 – Review Space And Support Limits
Available height, base footprint, and foundation capacity shape the final choice. Some spring isolation systems need more clearance, while low‑profile neoprene pads work in tight spaces. Also plan access so maintenance teams can inspect or change isolators without major disassembly.
Step 6 – Match Hardness And Dynamic Stiffness
For elastomeric mounts, Shore hardness affects how much they deflect under load and where the natural frequency sits. Dynamic stiffness tells us how the mount behaves under actual vibration, not just static weight. At RK Rubber Enterprise Co., we use this data to select or customize rubber cushion so the system avoids resonance and meets target isolation.
When customers share accurate load and layout data, we can provide clear recommendations and test information that support both performance and compliance documentation.
Measurable Benefits: How Proper Vibration Isolation Improves HVAC Performance

When vibration isolators are selected and installed correctly, the gains show up in both technical reports and financial statements. Many plants and buildings move from constant repairs to stable, predictable HVAC operation once proper isolation is in place.
Key measurable benefits include:
- Longer equipment lifespan.
With lower mechanical stress on bearings, shafts, and compressor internals, HVAC units can run thirty to fifty percent longer before major overhaul or replacement. Over a ten‑ to fifteen‑year planning window, this can keep expensive chillers and large fans in service well past the point where poorly isolated units would already be replaced.
- Lower maintenance costs.
Better isolation means fewer bearing changes, fewer refrigerant leaks due to cracked lines, and less time spent on repeated alignment work. Many facilities report maintenance savings in the range of twenty to forty percent for well‑isolated systems, along with fewer emergency callouts and less unplanned downtime during peak cooling months.
- Improved energy performance.
Machines that stay in alignment and operate on healthy bearings use less power. With proper vibration control, it is common to see five to fifteen percent better energy use compared with similar equipment installed on hard mounts. With local electricity costs, even the lower end of that range gives a strong payback.
On top of this, stable isolation supports:
- More consistent temperatures and humidity
- Fewer nuisance trips and control issues
- Quieter spaces and better comfort for occupants
- Less risk of damage to foundations and nearby sensitive equipment
RK Rubber Enterprise Co. supports these gains with high‑quality rubber compounds and tested spring designs that hold their properties over many years in Philippine conditions.
Conclusion
Good HVAC design is about more than picking the right capacity and controls. Without proper vibration isolation, even the best chiller or air handling unit can become a source of wasted energy, early failure, and ongoing complaints. Well‑chosen vibration isolators keep movement inside the machine, protect the building, and help systems run closer to their rated performance for a longer time.
By investing in quality isolation, we protect both the equipment and the structure that supports it. That means fewer major repairs, less noise in offices or hotel rooms, and a longer interval before expensive replacements appear in the budget. When we factor in lower energy use and reduced maintenance, the initial cost of good isolators often pays back many times over the life of the HVAC plant.
For facilities in the Philippines, the PEC and NFPA 110 already recognize how important proper vibration control is, especially around emergency power systems. Bringing the same care to all major HVAC equipment keeps projects safer, quieter, and easier to justify during audits and inspections. Facility managers, engineers, and contractors should review existing installations, check for proper vibration control, and specify isolation from the start on new projects.
At RK Rubber Enterprise Co., we support this work with a wide product range, from anti‑vibration rubber pads and neoprene strips to engineered metal‑bonded mounts and spring isolators. Our team helps match each product to real loads and conditions, giving customers both reliable performance and peace of mind.
FAQs
Question 1: What Is The Difference Between Elastomeric And Spring Vibration Isolators For HVAC Systems?
Elastomeric vibration isolators use rubber compounds to absorb higher‑frequency vibration, usually above fifteen to twenty hertz. They suit smaller and medium HVAC units, such as compressors, fan coil units, and packaged rooftop systems, where loads and deflections stay moderate. Spring isolators use steel coils to handle lower‑frequency vibration and heavier equipment, such as chillers and cooling towers. They provide greater deflection and better isolation for slow‑speed machines. The choice depends on operating speed, weight, and how much isolation the project needs, and RK Rubber Enterprise Co. offers both types with options for customization.
Question 2: Are Vibration Isolators Required By Law In The Philippines For HVAC Installations?
For emergency power supply systems, yes. PEC Chapter 7 points to NFPA 110, whose Rule 7.5 calls for vibration isolators between the rotating equipment and skid, or between the skid and the foundation. General HVAC equipment outside emergency systems may not always be named directly in the same way. However, manufacturers and industry groups such as EGSA and NEIS strongly discourage direct bolting without isolation. Following their guidance protects structural and equipment warranties and reduces the risk of damage or liability.
Question 3: How Do I Know What Size And Type Of Vibration Isolator I Need For My HVAC Equipment?
Sizing starts with accurate equipment data. You need the full operating weight including refrigerant, oil, and accessories; the rotating speed of fans or compressors; and the mounting layout. From there, check how weight is shared across the support points and what isolation level is needed for the space below or around the unit. Undersized isolators will compress too much and lose their function, while oversized units may not deflect enough and can cause instability. The best path is to consult manufacturer data and then work with a partner like RK Rubber Enterprise Co., where our technical team uses real load point measurements and site conditions to recommend the correct type and rating.
Question 4: Can Vibration Isolators Really Extend HVAC Equipment Lifespan And Reduce Energy Costs?
Yes, and the gains are measurable. By cutting vibration levels, you reduce wear on bearings, motors, and compressor parts, which can extend service life by thirty to fifty percent compared with rigid mounting. That same reduction in friction and misalignment often improves energy performance by about five to fifteen percent, because motors do not fight extra resistance. Maintenance needs usually drop by twenty to forty percent as leaks, bearing failures, and misalignment problems become less common. In many projects, the cost of proper vibration isolators pays back within two to three years through combined savings, especially when using RK Rubber’s durable compounds and tested designs.
Question 5: How Often Should Vibration Isolators Be Inspected Or Replaced?

We suggest at least one visual inspection each year. During this check, look for cracks, hardening, or excessive compression in rubber parts and make sure the equipment remains level on its supports. Quality elastomeric mounts often last ten to fifteen years, while well‑protected spring isolators can serve for fifteen to twenty years or more. Signs that replacement is needed include visible cracking, permanent flattening beyond design limits, and noticeable increases in transmitted vibration or noise. RK Rubber Enterprise Co. designs its products with strong resistance to weather, corrosion, and mechanical shock, which supports long service life under Philippine conditions.